Laygo architecture¶
 Laygo package structure
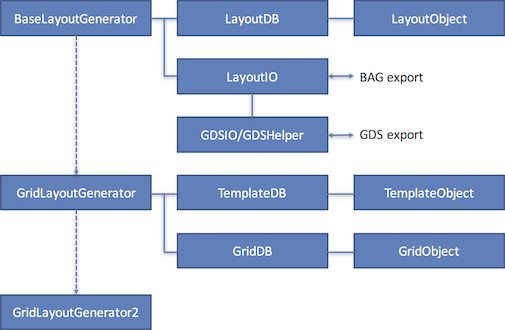
Laygo package structure
Laygo package has 10 submodules, classified into 4 categories; Generator, Database, Object, and IO.
Generator modules interact with user input (scripts) and command database and IO modules to do actual layout generation jobs. There are 2 generator modules implemented in laygo.
- BaseLayoutGenerator: generates layout on physical grids.
- GridLayoutGenerator: generates layout on abstract grids.
- GridLayoutGenerator2: improved version of GridLayoutGenerator. Not backward compatible.
Since the GridLayoutGenerator class is based on BaseLayoutGenerator, users may instantiate the GridLayoutGenerator even for physical grid tasks.
Database modules store the design hierarchary (as a form of Python dictionary). 3 types of Database modules are used.
- LayoutDB: stores layout data (Rects, Instances, Pins, …)
- TemplateDB: stores template data for placements
- GridDB: stores grid data for placements and routings
Object modules compose the database module and implement actual layout/template/grid components.
- LayoutObject: implements layout objects. Supported types are Rect, Pin, Text, and Instance.
- TemplateObject: implements templates.
- GridObject: implements grids. The GridObject class has PlacementGrid and RouteGrid as derived classes.
IO modules import/export generated layout data in various formats. While template and grid IO functions are embedded in TemplateDB and GridDB classes, separate modules are implemented for layout objects for their complexity.
- LayoutIO is used for importing / exporting layout data. Currently it supports 2 options: BAG and GDS. Yaml/OA/Skill/pyplot options will be supported in later versions.
- GDSIO is a dedicated class for GDS file support.